Article
Green Synthesis of Novel Silver Nanoparticles Using Salvia blepharophylla and Salvia greggii: Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Potential and Effect on Foodborne Bacterial Pathogens
Int. J. Mol. Sci.
(2024)
Abstract
In the face of evolving healthcare challenges, the utilization of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs)
has emerged as a compelling solution due to their unique properties and versatile applications. The
aim of this study was the synthesis and characterization of novel AgNPs (SB-AgNPs and SG-AgNPs,
respectively) using Salvia blepharophylla and Salvia greggii leaf extracts and the evaluation of their
antimicrobial, antioxidant, and antidiabetic activities. Several analytical instrumental techniques
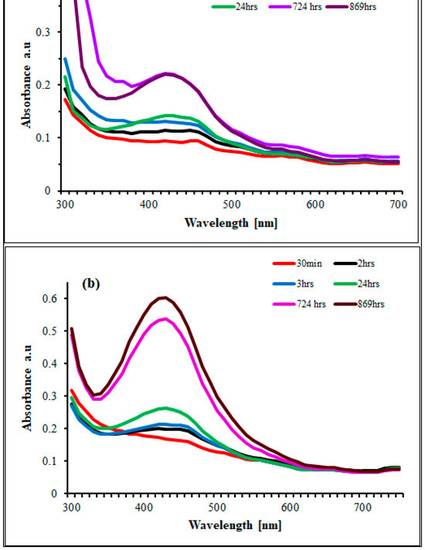
were utilized for the characterization of SB-AgNPs and SG-AgNPs, including UV–visible (UV-Vis)
spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), dynamic light scattering (DLS), Fourier transmission
infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX), and X-ray diffraction
(XRD). FTIR analysis identified various functional groups in the leaf extracts and nanoparticles,
suggesting the involvement of phytochemicals as reducing and stabilizing agents. High-resolution
TEM images displayed predominantly spherical nanoparticles with average sizes of 52.4 nm for
SB-AgNPs and 62.5 nm for SG-AgNPs. Both SB-AgNPs and SG-AgNPs demonstrated remarkable
antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes
and Gram-negative bacteria Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. SB-AgNPs and SG-AgNPs
also exhibited 90.2 ± 1.34% and 89.5 ± 1.5% DPPH scavenging and 86.5 ± 1.7% and 80.5 ± 1.2%
α-amylase inhibition, respectively, at a concentration of 100 μg mL−1. Overall, AgNPs synthesized
using S. blepharophylla and Salvia greggii leaf extracts may serve as potential candidates for antibacterial,
antioxidant, and antidiabetic agents. Consequently, this study provides viable solutions to
mitigate the current crisis of antibiotic resistance and to efficiently combat antimicrobial infections
and Type 2 diabetes.
Keywords
- Salvia blepharophylla; Salvia greggii; antioxidant; antidiabetic; antibacterial; foodborne pathogens
Disciplines
Publication Date
Winter January 11, 2024
DOI
https://doi.org/ 10.3390/ijms25020904
Citation Information
Addisie Geremew, John Gonzalles, Elisha Peace, Sela Woldesenbet, et al.. "Green Synthesis of Novel Silver Nanoparticles Using Salvia blepharophylla and Salvia greggii: Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Potential and Effect on Foodborne Bacterial Pathogens" Int. J. Mol. Sci. Vol. 25 (2024) Available at: http://works.bepress.com/addisie-geremew/17/
Creative Commons license

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons CC_BY International License.
