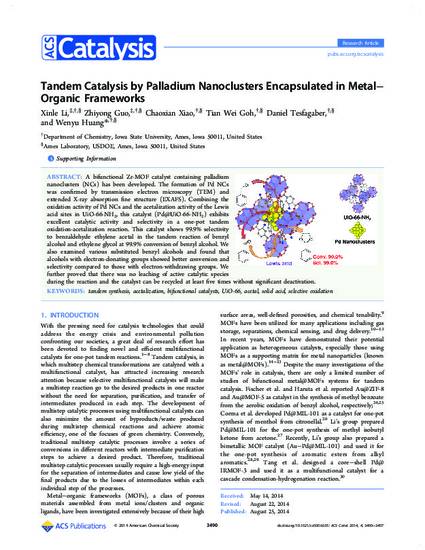
A bifunctional Zr-MOF catalyst containing palladium nanoclusters (NCs) has been developed. The formation of Pd NCs was confirmed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS). Combining the oxidation activity of Pd NCs and the acetalization activity of the Lewis acid sites in UiO-66-NH2, this catalyst (Pd@UiO-66-NH2) exhibits excellent catalytic activity and selectivity in a one-pot tandem oxidation-acetalization reaction. This catalyst shows 99.9% selectivity to benzaldehyde ethylene acetal in the tandem reaction of benzyl alcohol and ethylene glycol at 99.9% conversion of benzyl alcohol. We also examined various substituted benzyl alcohols and found that alcohols with electron-donating groups showed better conversion and selectivity compared to those with electron-withdrawing groups. We further proved that there was no leaching of active catalytic species during the reaction and the catalyst can be recycled at least five times without significant deactivation.
Available at: http://works.bepress.com/wenyu_huang/6/

Reprinted (adapted) with permission from ACS Catal., 2014, 4 (10), pp 3490–3497). Copyright 2014 American Chemical Society.