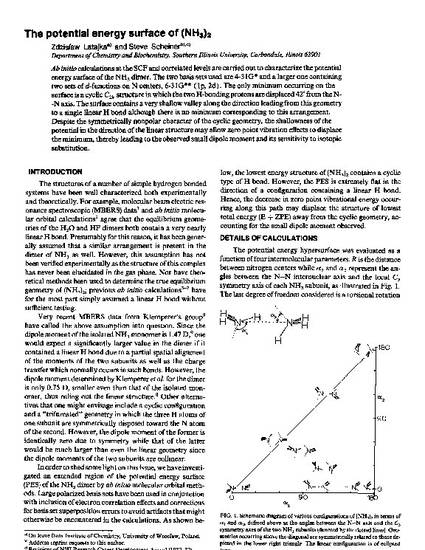
Ab initio calculations at the SCF and correlated levels are carried out to characterize the potential energy surface of the NH3 dimer. The two basis sets used are 4‐31G∗ and a larger one containing two sets of d‐functions on N centers, 6‐31G∗∗ (1p, 2d). The only minimum occurring on the surface is a cyclic C2h structure in which the two H‐bonding protons are displaced 42° from the N‐‐N axis. The surface contains a very shallow valley along the direction leading from this geometry to a single linear H bond although there is no minimum corresponding to this arrangement. Despite the symmetrically nonpolar character of the cyclic geometry, the shallowness of the potential in the direction of the linear structure may allow zero point vibration effects to displace the minimum, thereby leading to the observed small dipole moment and its sensitivity to isotopic substitution.

Originally published by American Institute of Physics in the Journal of Chemical Physics.
Publisher's PDF can be accessed through the remote link.