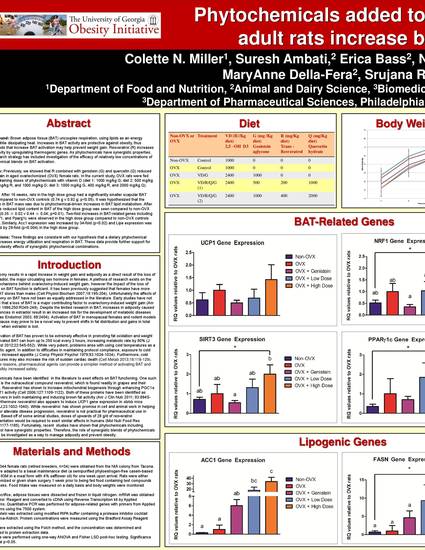
Background: Brown adipose tissue (BAT) uncouples respiration, using lipids as an energy source while dissipating heat. Increases in BAT activity are protective against obesity, thus compounds that increase BAT activation may help prevent weight gain. Resveratrol (R) increases BAT activity by upregulating thermogenic genes. As phytochemicals have synergistic properties, our research strategy has included investigation of the efficacy of relatively low concentrations of phytochemical blends on BAT activation. Methods: Previously, we showed that R combined with genistein (G) and quercetin (Q) reduced weight gain in aged ovariectomized (OVX) female rats. In the current study, OVX rats were fed diets containing doses of phytochemicals with vitamin D (diet 1: 1000 mg/kg G; diet 2: 500 mg/kg G, 200 mg/kg R, and 1000 mg/kg Q; diet 3: 1000 mg/kg G, 400 mg/kg R, and 2000 mg/kg Q). Results: After 16 weeks, rats in the high dose group had a significantly smaller scapular BAT depot compared to non-OVX controls (0.74 g v 0.92 g; p
Available at: http://works.bepress.com/srujana_rayalam/1/
