Article
Implementation of a Protocol: Dexmedetomidine for Use in Long-Term Procedural Sedation in Non-Intubated Pediatric Patients
Journal of Pediatric Nursing
(2021)
Abstract
The objective of this quality initiative was to evaluate the process of implementing a new protocol using the Iowa model and evidence-base interventions. The first aim included deploying a protocol guiding sedation with dexmedetomidine for up to 24 h; the procedure involved non-intubated pediatric patients in the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) while monitored by certified registered nurses. Dexmedetomidine is supported within the literature to be a safe and effective medication for pediatric patients, exceeding 24 h, without the adverse event of respiratory depression. The second aim was to then evaluate the implementation process.
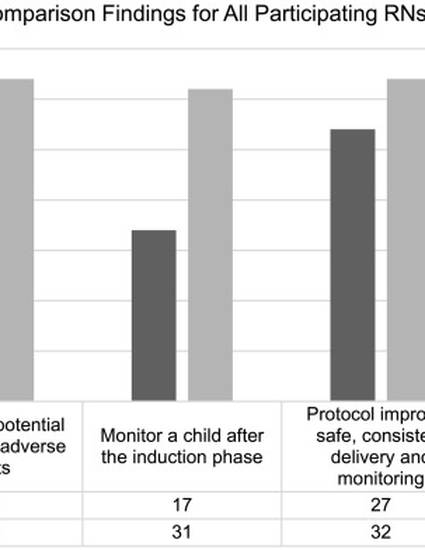
A pre-post educational approach was used, over a five-month period. Thirty-two nurses were educated and surveyed on their knowledge and attitudes regarding the use and administration of dexmedetomidine. The evaluation of pre and post knowledge surrounding dexmedetomidine was concluded following the post-survey. The evaluation of pre-post education showed, greater than 90% of the attending nurses, had an increase in their knowledge and understanding of safe use and monitoring for dexmedetomidine sedations in children.
This quality initiative further supports effective application of evidence-based interventions. Moreover, using the Iowa model allowed for the effective execution in driving change, promoting sustainability, and improving safety in the delivery of care for pediatric patients receiving dexmedetomidine for long-term sedation.
Keywords
- Sedation,
- Dexmedetomidine,
- Pediatric Patients,
- Adverse events,
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS)
Disciplines
Publication Date
Spring May, 2021
DOI
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedn.2020.11.005
Citation Information
Sherri Fannon. "Implementation of a Protocol: Dexmedetomidine for Use in Long-Term Procedural Sedation in Non-Intubated Pediatric Patients" Journal of Pediatric Nursing Vol. 58 (2021) p. 39 - 43 Available at: http://works.bepress.com/sherri-fannon/2/
