Article
Multivalent Li-Site Doping of Mn Oxides for Li-Ion Batteries
Journal of Physical Chemistry C
(2015)
Abstract
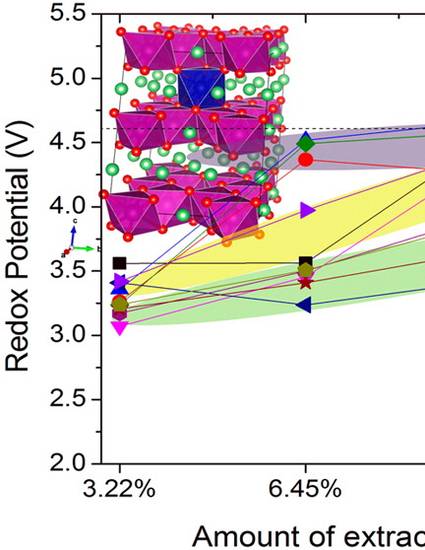
Doping is the most common strategy to suppress the intrinsic structural instability of several families of cathode materials, thus improving their electrochemical performance. During the electrode synthesis, the dopants have a low probability to occupy cationic Li sites, but it is well-known that, during the normal operation of the battery, such probability increases via inter- or intralayer diffusion. In this work, we investigate the effect of 10 Li-site cationic dopants (Mg, Ti, V, Nb, Fe, Ru, Co, Ni, Cu, Al) on the electrochemical properties of Li2MnO3 and LiMnO2 cathode materials using density functional theory. Our results show that, although Mn sites are thermodynamically favorable over Li-site doping, the small thermodynamic barriers between both configurations can be easily overcome during the material synthesis and/or the extraction/insertion of Li during the cycling process of the battery. Also, due to charge balance and diffusion channel opening, some of the Li-site dopants were found to act as activation centers, facilitating the diffusion of the neighboring Li ions. Additionally, they constitute a new activation mechanism for the electrochemically inactive Li2MnO3. These findings explain some of the unusual observed effects of Li-site doping, as compared to the more common transition-metal site doping, and therefore provide a new direction toward the optimization of the electrochemical performance of layered oxide cathode materials.
Keywords
- Impurities,
- Transition metals,
- Diffusion,
- Doping Ions
Disciplines
Publication Date
September 9, 2015
DOI
10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b06844
Publisher Statement
SJSU users: Use the following link to login and access the article via SJSU databases.
Citation Information
Fantai Kong, Roberto C. Longo, Dong-Hee Yeon, Jaegu Yoon, et al.. "Multivalent Li-Site Doping of Mn Oxides for Li-Ion Batteries" Journal of Physical Chemistry C Vol. 119 Iss. 38 (2015) p. 21904 - 21912 ISSN: 1932-7447 Available at: http://works.bepress.com/santosh-kc/20/