Article
Improvement of Ti/TiN Interfacial Shear Strength by Doping– A First Principles Density Functional Theory Study
Applied Surface Science
(2020)
Abstract
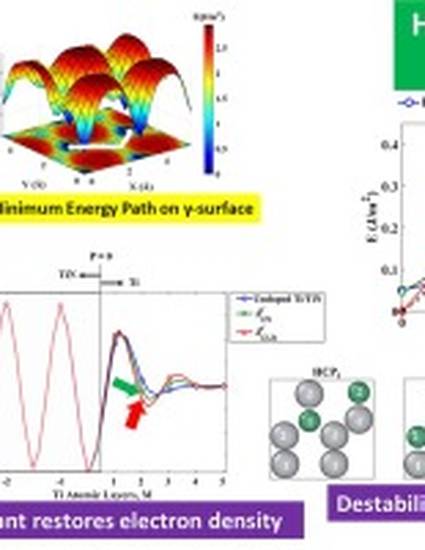
The dependence of interfacial shear resistance on the substitutional doping of Al, V and Cr at the Ti/TiN interface was studied using first principles Density Functional Theory. Only Al dopants had negative enthalpies of mixing in Ti and at the Ti/TiN interface. Generalized stacking fault energies (GSFE) were calculated and their barriers were used as an estimate of shear resistance. The addition of Al increased the GSFE barriers of pure Ti when they were in adjacent atomic layers. It was found that when Al atoms were in contact, they had a destabilizing effect that led to the increased barriers in certain configurations. Near the Ti/TiN interface, the presence of one or two Al dopants increased the GSFE barrier by drawing some of the electron charge from the ceramic N atoms into the Ti phase. There was a general correlation between higher GSFE barriers and Al concentration at the Ti/TiN interface, which were attributed to both of the described effects: destabilizing Al-Al interactions and Al drawing electron density from the ceramic into the Ti phase.
Keywords
- metal/ceramic interfaces,
- doping,
- nanocomposites,
- DFT,
- charge density
Disciplines
Publication Date
July, 2020
DOI
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146185
Citation Information
Abu Shama Mohammad Miraz, Eboni Williams, Wen J. Meng, B. R. Ramachandran, et al.. "Improvement of Ti/TiN Interfacial Shear Strength by Doping– A First Principles Density Functional Theory Study" Applied Surface Science Vol. 517 (2020) p. 146185 Available at: http://works.bepress.com/ramu-ramachandran/12/
