Article
Nectar antimicrobial compounds and their potential effects on pollinators
Current Opinion in Insect Science
(2021)
Abstract
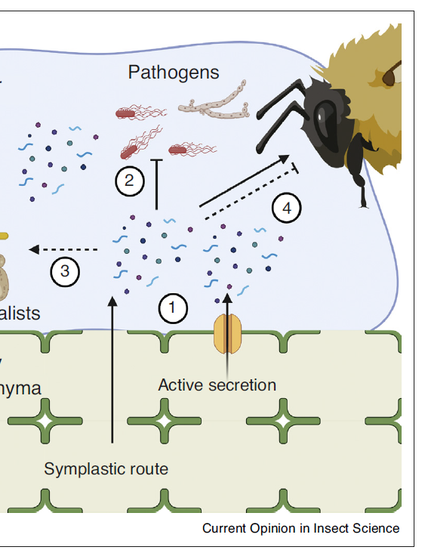
Nectar is a sugary, aqueous solution that plants offer as a reward to animal mutualists for visitation. Since nectars are so nutrient-rich, they often harbor significant microbial communities, which can be pathogenic, benign, or even sometimes beneficial to plant fitness. Through recent advances, it is now clear that these microbes alter nectar chemistry, which in turn influences mutualist behavior (e.g. pollinator visitation). To counteract unwanted microbial growth, nectars often contain antimicrobial compounds, especially in the form of proteins, specialized (secondary) metabolites, and metals. This review covers our current understanding of nectar antimicrobials, as well as their interplay with both microbes and insect visitors.
Disciplines
Publication Date
Spring April 1, 2021
Citation Information
Anthony J. Schmitt, Rahul Roy and Clay J. Carter. "Nectar antimicrobial compounds and their potential effects on pollinators" Current Opinion in Insect Science (2021) Available at: http://works.bepress.com/rahul_roy/12/
