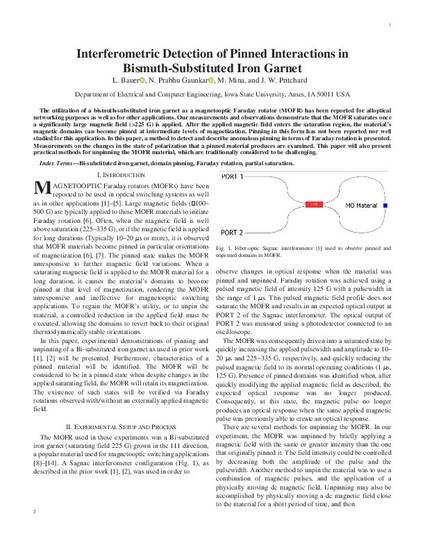
The utilization of a bismuth-substituted iron garnet as a magnetooptic Faraday rotator (MOFR) has been reported for all-optical networking purposes as well as for other applications. Our measurements and observations demonstrate that the MOFR saturates once a significantly large magnetic field (>225 G) is applied. After the applied magnetic field enters the saturation region, the material's magnetic domains can become pinned at intermediate levels of magnetization. Pinning in this form has not been reported nor well studied for this application. In this paper, a method to detect and describe anomalous pinning in terms of Faraday rotation is presented. Measurements on the changes in the state of polarization that a pinned material produces are examined. This paper will also present practical methods for unpinning the MOFR material, which are traditionally considered to be challenging.
Available at: http://works.bepress.com/mani_mina/29/

This article is published as Bauer, L., Prabhu Gaunkar, N., Mina, M., Pritchard, J.W., Interferometric Detection of Pinned Interactions in Bismuth-Substituted Iron Garnet. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics.; 2019; Doi:10.1109/TMAG.2019.2892437. Posted with permission.