Introduction: Facebook, one of the worlds' most popular online social networks, is easy to access and cost-effective. Its use to enhance individual's physical activity (PA) participation should be examined. This research reviews the effectiveness and successful features of Facebook for influencing PA behaviors in young adults (Study 1), and empirically examines the efficacy of the features purported in increase PA via a Facebook intervention (Study 2).
Methods: In Study 1, PubMed, Medline, SPORT Discus, ERIC, and Embase were searched for articles that identified successful features and effectiveness of Facebook PA interventions published between January 2005 and February 2022. In Study 2, a 4-week Facebook PA intervention with University students was conducted using features identified in Study 1. The PA behaviors with objective (ActiGraph) and subjective (questionnaire) measures, perceived PA level, stage of readiness, effectiveness, and efficiency of Facebook were examined.
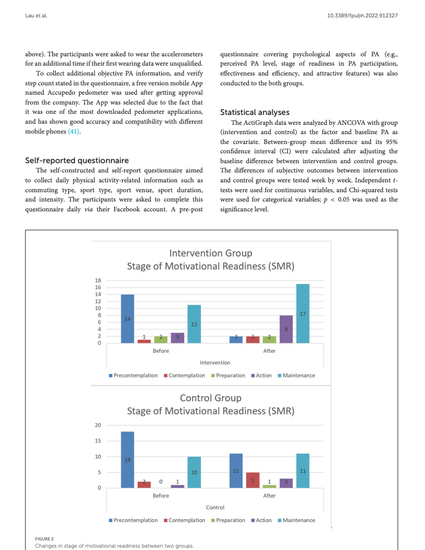
Results: Study 1 concluded that the most effective strategies for producing significant PA changes in young adults using a PA Facebook intervention included the following: Adding behavior modification (goal setting and self-monitoring), using influence agents, recruiting members of an existing network with the snowball technique, being attentive to group size, enhancing social support with motivational quotes, interactive posts, opinion polls, increasing tailored feedback, and providing educational information. Study 2 found no significant difference in PA between the intervention and the control groups, as measured objectively, but the subjective reporting of PA behavior was higher in the intervention group. Compared to the control group, the Facebook PA intervention group reported more positive change in perceived stage of readiness in PA participation, commuting type, sport type, sport venue, sport emotion, and fast breathing or sweating. When features were ranked by the Facebook PA intervention group, motivation (supports from your friends) and tailored feedback (the responses from your friends are really personal and fits you) were the top two ranked features.
Conclusion: The use of influence agents in the Facebook PA intervention could address exercise preference and facilitate higher program engagement. Significant differences related to commuting type, sport types, sport venue barriers, and exercise intensity across groups were noteworthy and warrant additional investigation in the future.
Available at: http://works.bepress.com/lynda_ransdell/76/
