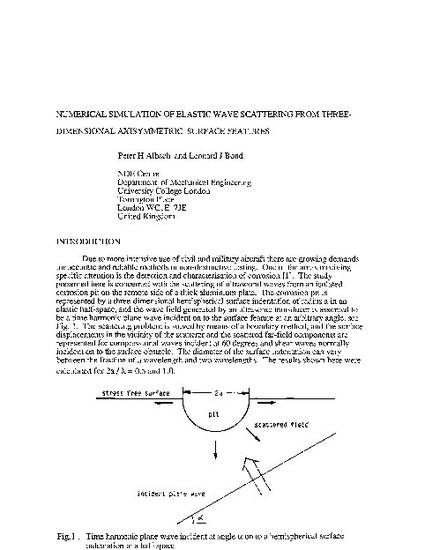
Due to more intensive use of civil and military aircraft there are growing demands for accurate and reliable methods in non-destructive testing. One of the areas receiving specific attention is the detection and characterisation of corrosion [1]. The study presented here is concerned with the scattering of ultrasound waves from an isolated corrosion pit on the remote side of a thick aluminium plate. The corrosion pit is represented by a three-dimensional hemispherical surface indentation of radius a in an elastic half-space, and the wave field generated by an ultrasonic transducer is assumed to be a time harmonic plane wave incident on to the surface feature at an arbitrary angle, see Fig. 1. The scattering problem is solved by means of a boundary method, and the surface displacements in the vicinity of the scatterer and the scattered far-field components are represented for compressional waves incident at 60 degrees and shear waves normally incident on to the surface obstacle. The diameter of the surface indentation can vary between the fraction of a wavelength and two wavelengths. The results shown here were calculated for 2a/λ = 0.5 and 1.0.
Available at: http://works.bepress.com/leonard_bond/27/
