Article
Climate-induced range overlap among closely related species
Nature Climate Change
(2015)
Abstract
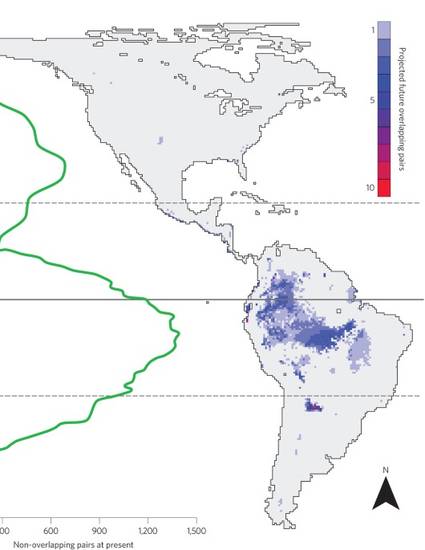
Contemporary climate change is causing large shifts in biotic distributions1, which has the potential to bring previously isolated, closely related species into contact2. This has led to concern that hybridization and competition could threaten species persistence3. Here, we use bioclimatic models to show that future range overlap by the end of the century is predicted for only 6.4% of isolated, congeneric species pairs of New World birds, mammals and amphibians. Projected rates of climate-induced overlap are higher for birds (11.6%) than for mammals (4.4%) or amphibians (3.6%). As many species will have difficulty tracking shifting climates4, actual rates of future overlap are likely to be far lower, suggesting that hybridization and competition impacts may be relatively modest.
Disciplines
Publication Date
July, 2015
DOI
https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate2699
Citation Information
M. Krosby, C. B. Wilsey, J. L. McGuire, Jennifer Duggan, et al.. "Climate-induced range overlap among closely related species" Nature Climate Change Vol. 5 (2015) p. 883 - 886 Available at: http://works.bepress.com/jennifer-duggan/13/
