Presentation
Risk of thrombocytopenia in patients on telavancin
ASHP Midyear
(2016)
Abstract
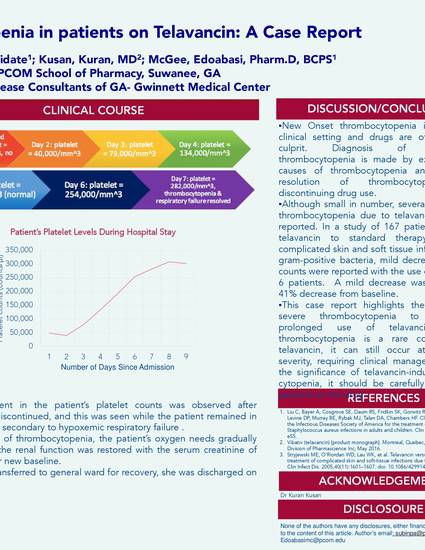
Telavancin is a glycopeptide antimicrobial indicated for patients with complicated SSTI and hospital acquired or ventilator acquired bacterial pneumonia. Thrombocytopenia is a very rare adverse effect of telavancin and few studies have evaluated its significance. This report presents such a case associated with telavancin use from the clinical practice of authors. A 68-year-old female was admitted to hospital due to shortness of breath. She was found to have bilateral pulmonary infiltrate with questionable CHF and pneumonia/pneumonitis and consequent acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. She was hypoxic, requiring 100 percent nonrebreather mask, and had a history of heavy tobacco abuse of smoking about 60 packs a year. Her past medical history was significant for chronic heart failure, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, chronic lymphedema in left lower limb, and breathing disorder. The patient presented with a severe thrombocytopenia of unknown etiology. On admission, the platelet count was 49,000/mm3. The patient had been on telavancin at an outpatient clinic for the past 21 days through her right chest wall tunneled PICC line for a left lower extremity cellulitis. After admission, telavancin was discontinued and replaced by Zosyn in order to empirically treat for pneumonia. On June 21st, 2016, the patient’s platelet count was 49,000/mm3 without signs of bleeding. On June 22nd, 2016, , the platelet count decreased even further to 40,000/mm3.Two days after discontinuing telavancin on June 23rd,the patient’s platelet counts improved to 79,000/mm3, and restored to normal levels by the 25th. The improvement in the patient’s platelet counts was observed after telavancin was discontinued, and this was seen while the patient remained in critical condition secondary to hypoxemic respiratory failure through the 27th. After resolution of thrombocytopenia, the patient’s oxygen needs gradually decreased and the renal function was restored with the serum creatinine of 2.0 mg/dL as her new baseline. After getting transferred to general ward for recovery, she was discharged on July 3rd. This case report highlights the potential for incidence of thrombocytopenia to occur with prolonged use of telavancin. Although thrombocytopenia is a rare complication of telavancin, it can still occur at an alarming severity, requiring clinical management. Due to its significance, it should be carefully monitored in patients on the drug.
Disciplines
Publication Date
December, 2016
Location
Las Vegas, NV
DOI
https://www.ashp.org/-/media/assets/meetings-events/docs/mcm16-student-poster-abstracts-session-board.ashx?la=en&hash=B03789F7D394B5DC1B4F0D0902C3D3FDAF2DDDE0
Citation Information
Su Bin Park, Kuran Kusan and Edo-abasi U. McGee. "Risk of thrombocytopenia in patients on telavancin" ASHP Midyear (2016) Available at: http://works.bepress.com/edo-abasi_mcgee/13/
