Presentation
Validity of Wearable Activity Monitors for Estimation of Resting Energy Expenditure in Adults
Research Presentations
Document Type
Poster
Publication Date
1-1-2015
Disciplines
Abstract
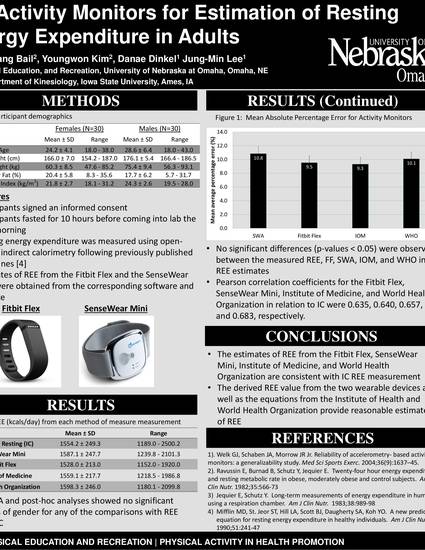
• Wearable accelerometers have become the standard method for assessing physical activity for both individuals and field-based research [1]. These new devices allow consumers to have the ability to estimate total energy expenditure and track it over time. • Resting Energy Expenditure plays a critical role in estimating daily total energy expenditure as it contributes 60-70% of total energy expenditure [2,3]. • Little to no information is available to substantiate the validity of these consumer-based activity monitors under free-living conditions.
Citation Information
Zachary Motz, Yang Bail, Youngwon Kim, Danae M. Dinkel, et al.. "Validity of Wearable Activity Monitors for Estimation of Resting Energy Expenditure in Adults" (2015) Available at: http://works.bepress.com/danae-dinkel/58/

ACSM 2015