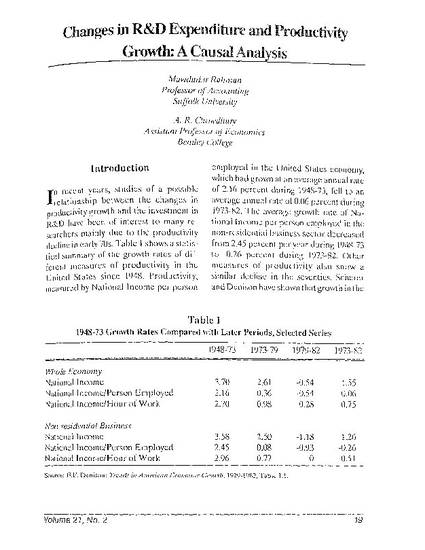
A study was conducted to directly test the presence of causal relationship between changes in research and development (R&D) expenditure and productivity growth. Granger causality tests are performed using annual time series data for the period 1956-1983. Three measures of productivity are used -- National Income, National Income per person employed, and National Income per hour of work in the nonresidential business sector. Results show that changes in R&D expenditure affect the growth rate of the 3 productivity measures with different degrees of intensity. National Income per hour of work shows the highest growth rate, with the peak effect occurring in the 2nd year and maintaining a high growth rate through the 4th year. National Income shows the 2nd highest growth rate. The growth rate of all 3 measures decreases significantly in the 4th year. These results suggest that when projecting economic growth, planners should take R&D investment levels into account.
Available at: http://works.bepress.com/abdur_chowdhury/100/

Published version. Arkansas Business and Economic Review, Vol. 21, No. 2 (Spring 1988): 19-27. Publisher link. © 1988 University of Arkansas, College of Business Administration, Bureau of Business and Economic Research. Used with permission.
Abdur Chowdhury was affiliated with Bentley College at the time of publication.